Microscope Stages
A microscope stage, also known as an XY microscope stage or Z microscope stage, is a platform that holds and moves a sample in x, y and z motion, enabling precise positioning and observation under a microscope. They come in various types, such as rotating stages, motorized stages, and translation stages. Depending on the direction of movement, microscope stages are classified into XY stages and Z focusing stages. We have created a unique stage architecture by embedding high-performance controller within the stage.
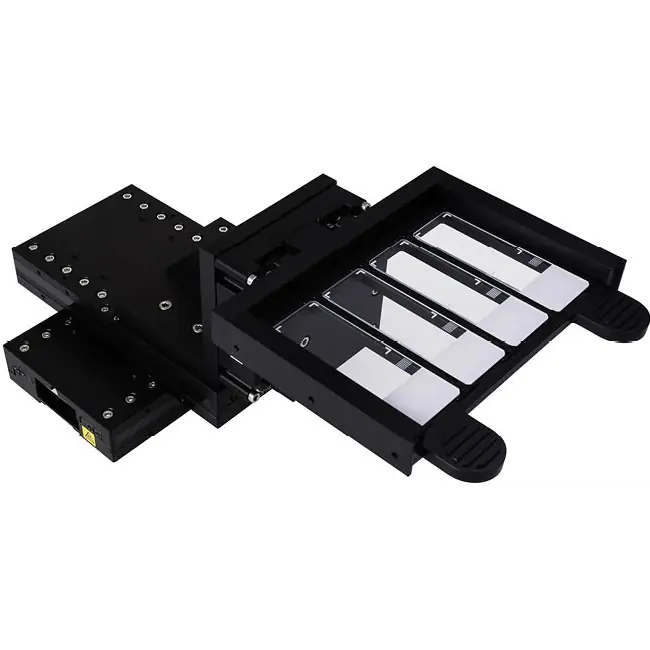
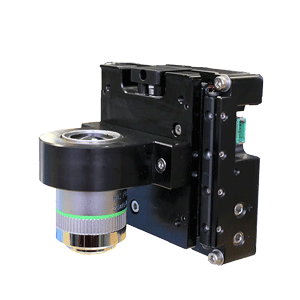
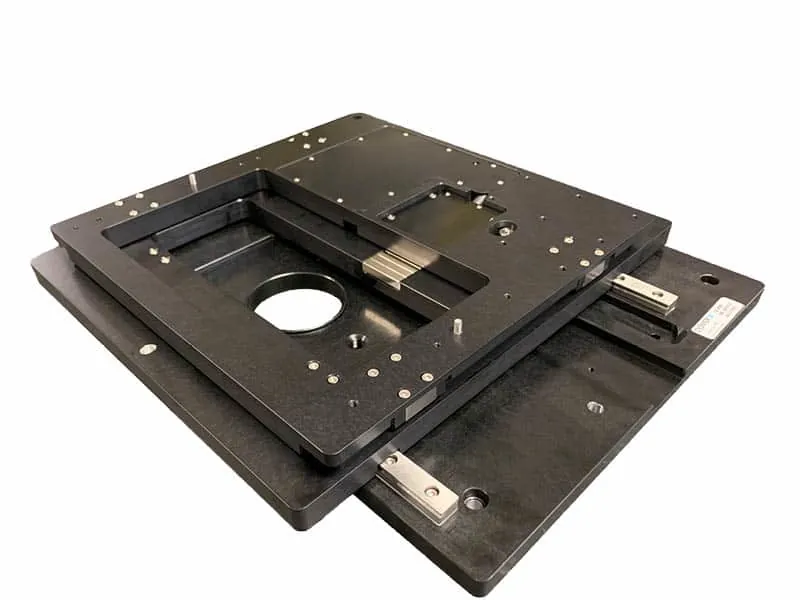
The SmartStage™ Open Frame stage, is the first open aperture linear motor stage with an embedded controller physically integrated inside the stage.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 115 x 75 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The award winning SmartStage™ XY stage offers high precision and includes an embedded controller inside the stage.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 200 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
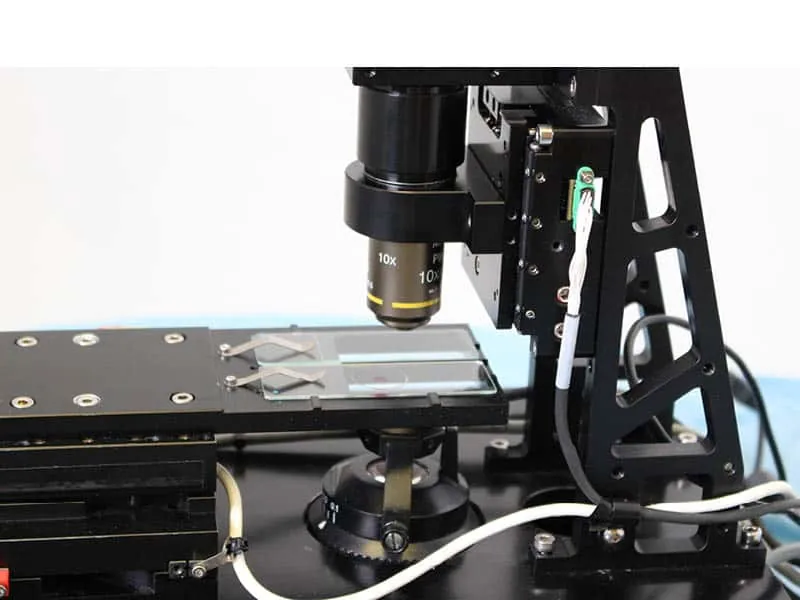
The DOF™ stage is optimized for objective focusing with increased travel, higher bandwidth, and lower cost than piezo stages.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 5 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 1.25 nm |
| 2 | Repeatability | < 50 nm |
| 3 | Bandwidth | > 225 Hz |
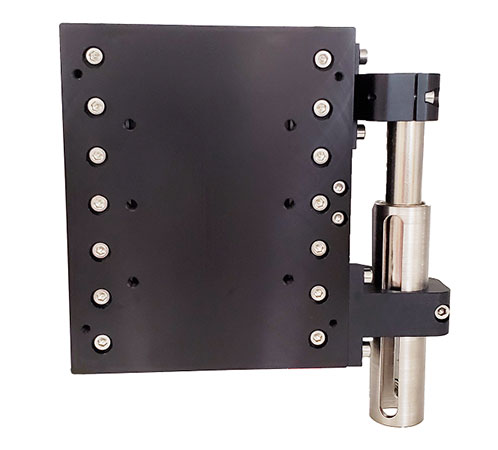
The SmartStage Z-50 provides a unique combination of travel distance, and precision, for vertical Z stage applications.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 5 nm |
| 2 | Accuracy | 10 μm |
| 3 | Repeatability | .8 μm |
Microscope Stage Resources
Whitepapers
This whitepaper provides an introduction to the SmartStage™ XY platform and a comparison to alternative technologies to show why this technology is already transforming automated digital microscopy.
This white paper addresses high performance Z axis focusing for automated microscopy, along with some recent innovations in this space.
Videos
Discover the SmartStage™ XY microscope stage and its cutting-edge design, offering precise motion and exceptional reliability. Explore its standout features and learn how it seamlessly integrates with our other products to enhance your system’s performance.
Discover the easiest way to obtain perfect images with your automated digital microscope. Open the box, add your objective and start focusing.
Custom Microscope Stage Capabilities
Dover Motion has more than 25 years of experience working with OEMs to optimize motion for automated digital microscopy including objective focusing and moving samples on slides, well plates, or flow cells.
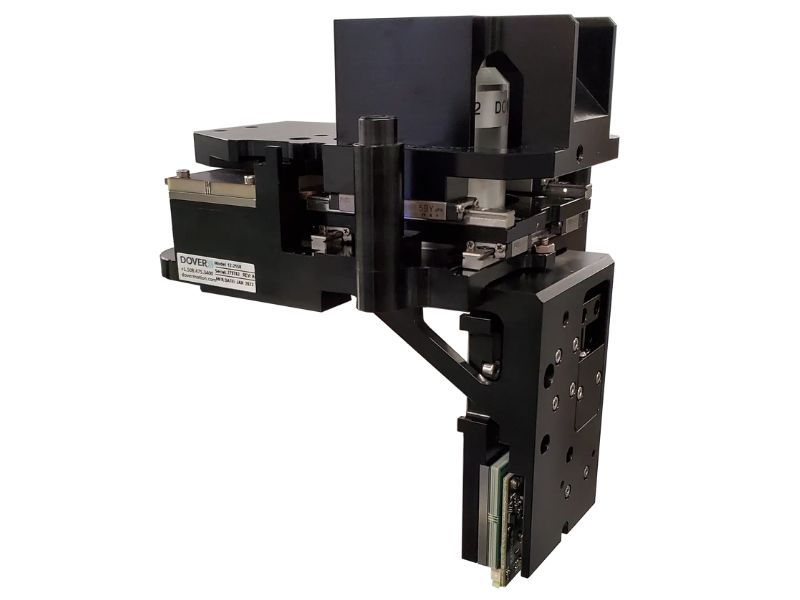
Our engineers developed unique motion control architectures for precision motion systems specifically tailored to the needs of OEMs developing microscope-based systems and instruments relying on optical imaging as the analytical detection technique. For applications requiring synchronized control across three axes, we offer a wide variety of standard and custom XYZ stages. These stages integrate our XY stages with high-performance vertical Z stages, delivering seamless and compact multi-axis motion in one unified solution for precise sample alignment, faster imaging, and improved throughput in complex microscopy applications.
Whether your project requires a customization to a standard product or a completely custom microscope stage design, we’ll collaborate with your team to ensure we hit the most challenging design, cost, and schedule targets.
- XY Stages moving a flow cell
- Z stage for objective focusing
- Integrated laser autofocus
- Automated Rotary filter changer
Speak with an Engineer about your custom application.
- Fast Linear Motors
- Built in controller
- High Resolution encoder feedback
Speak with an Engineer about your custom application.
- DOF Objective focusing
- Linear Motor XY for slide positioning
Speak with an Engineer about your custom application.
"The SmartStage XY linear motor stages surprised us with their speed and silence. They have handily met our need for fast, accurate movements, and long holding stability. We love the internally protected optical encoders, making the stages more reliable and easier to work with."
- Associate Director of Engineering, Life Science OEM

Microscopy Learning Center
We’ve created this library of resources to connect you the latest information on microscopy and to guide you to expert insights, microscope stage product documentation, and reviews of key concepts and considerations that will accelerate your next discovery or breakthrough.
Whitepapers
Optimize the performance and cost of your automated optical imaging system with 6 key equations for selecting an imaging sensor, objective lens, Z-focusing nano-positioning stage and XY sample positioning motion.
For a variety of life science applications, images at multiple Z planes within the sample must be acquired. In this white paper, we examine techniques to maximize Z stack imaging throughput.
Case Studies
Through concurrent and collaborative engineering, Dover Motion designed a compact custom XYZ stage solution to produce high-precision cell imaging in parallel with the instrument design.
Dover Motion worked closely with Invetech to define the motion system requirements and tightly integrate the hardware in the overall instrument design.
Videos
View some of our educational videos here.
Topics that will be covered are selecting the right type of sensor and sensor size, magnification, field of view, pixel size, resolution, depth of field, and numerical aperture for digital microscopy.
Depth of field is an important criteria for selecting the precision and resolution of focusing stages for automated imaging applications. This video explains what depth of field refers to for objective focusing.
When designing complex systems, there are a lot of options to consider. In this video, we explain the XY stage for sample positioning, and Z stage for precision microscope objective focusing motion.
This video covers key formulas for selecting the optimal imaging sensor and microscope objective for your digital imaging application.
Anatomy of a Microscope
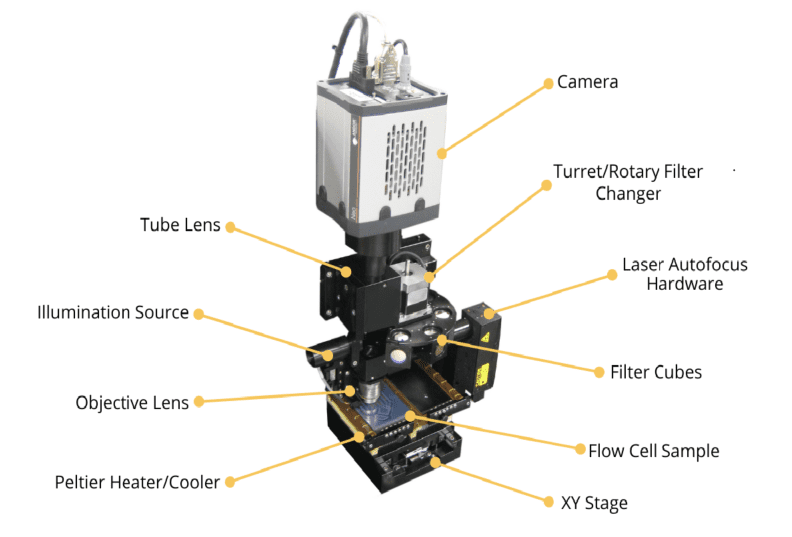
Tube Lens: An optical element that focuses the parallel light of an infinity corrected objective onto the image sensor surface.
Illumination Source: The illumination source sends light to the reflective mirror to illuminate the sample in epi-fluorescence imaging.
Objective Lens: The primary optical component of an imaging microscope, and responsible for magnification and focusing when moved relative to the sample.
Peltier Heater/Cooler: Helps modulate the temperature of the sample and ensures fast and precise temperature switch.
Camera: A central part of the automated digital microscope which has an image sensor to convert the reflected light into a digital image.
Turret/Rotary Filter Changer: A sub-assembly that mounts several objectives or fluorescent filters which can then be either manually or automatically rotated into position.
Laser Autofocus Hardware: Emits a beam of light from which the distance to the object can be determined and the correct focus or image point of a selected area is identified.
Filter Cubes: Allows specific wavelengths of light to pass through to permit high contrast fluorescent imaging.
Flow Cell Sample: The specimen that will be inspected, imaged, and analyzed by the automated digital microscope. Other sample types include slides, well plates, and custom microfluidic chips.
XY Microscope Stage: Used to position the sample (slides, flow cells, well plates, etc.) being imaged or analyzed under a microscope allowing motion in two degrees of freedom.