Single Axis Linear Stage
A single-axis linear stage provides precise automated positioning along a single axis of motion. It consists of a base, a movable platform, and a motor that drives the platform along a guided path. Single axis linear stages are used in applications requiring high-accuracy positioning and smooth motion, such as microscopy & imaging, DNA sequencing & genomics, optical metrology, and cell analysis & sorting.
At Dover Motion, we have created a unique single axis stage architecture by embedding high-performance precision electronics required to control motion within the stage without increasing its size. Explore our range of single axis linear motor and lead screw driven linear stages below.

Linear Motor Stages
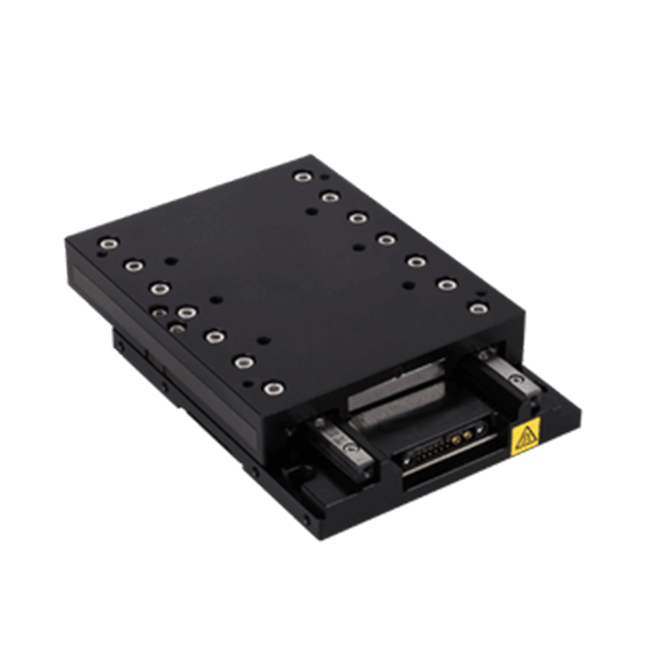
The SmartStage™ linear stage is our single axis stage with a built-in controller. It is available in a range of travel sizes and options.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 200 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The MMX™ series miniature direct drive linear motor stage has a low profile design with high power linear servo motor options.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 25 - 150 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | < ± 3 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.4 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The MAG™ series servo linear actuator uses a moving magnet design and linear servo motor to deliver high power and high performance.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 250 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 3 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 75 kg |
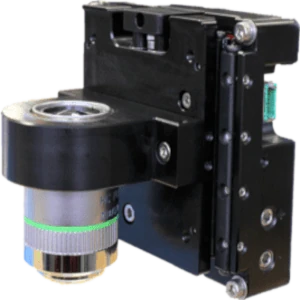
The DOF series objective focusing stage is our single axis linear stage optimized for optical microscopy applications.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 5-9 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 1.25 nm |
| 2 | Repeatability | < 50 nm |
| 3 | Bandwidth | > 225 Hz |
The SmartStage Z-50 provides a unique combination of 50-mm travel and 5 nm resolution for vertical Z stage applications.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 5 nm |
| 2 | Accuracy | 10 μm |
| 3 | Repeatability | .8 μm |
Lead Screw Driven Stages
Our elevator wedge ZE stage provides a small footprint with a 200-millimeter-square moving table. It is designed for wafer inspection, scanning, and probing applications
| wdt_ID | Travel | 12 - 38 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 15 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 1.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The LM™ series linear motion slide is a low-cost, single axis linear stage with crossed roller ways and stepper motor.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 300 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 15 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 1.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 175 kg |
The LMB™ series ball screw linear actuator is a high-precision, single-axis stage with crossed roller bearing and improved duty cycle, life, and speed.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 300 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 8 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 175 kg |
The FM™ series is a ball screw linear stage with a stiffer table and larger crossed roller bearings.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 100 - 350 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 5 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 1.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 115 kg |
Single Axis Linear Stage Guide
What is a single axis linear stage?
A single axis linear stage consists of a base, motion mechanism, guiding, and feedback systems. Let’s explore what each of these components does.
- Base and Moving Table:
- The base remains fixed, while the moving platform travels along a guided path.
- Motion Mechanism:
- Ball Screw or Lead Screw: As the screw rotates, the nut on the screw translates rotational motion into linear motion, pushing or pulling the platform.
- Linear Motor: A non-contact direct drive motor generates force directly to the moving platform, eliminating mechanical transmission parts and providing smoother motion.
- Stepper or Servo Motor: These are often used to control the stage's motion, providing precise control over position and speed.
- Guiding System:
- Linear guides or bearings (e.g., crossed roller bearings) ensure smooth and accurate movement of the platform, preventing any deviation from the path.
- Feedback System:
- Encoders or sensors monitor the position of the moving platform, providing real-time feedback to the control system for adjustments. They ensure high accuracy and repeatability of the stage.
How does single axis linear stage work?
A single-axis linear stage works by translating rotational motion from a motor or actuator into precise linear movement along a single axis (X, Y, or Z). It achieves this by using a combination of a drive mechanism and a guide system to ensure smooth, controlled, and accurate motion.
What are the different types of single-axis linear stages?
Single-axis linear stages can be categorized into different types based on drive mechanism and operating control methods.
The type of drive mechanism determines the performance of linear stages, with options like ball screw/lead screw and linear motor, each offering unique advantages in terms of speed, precision, and load capacity.
- Ball Screw and Lead Screw Linear Stages
These stages use a rotary motor and screw mechanism with rolling ball bearings to convert rotary motion into linear motion. - Linear Motor Stages
Powered by a direct-drive linear motor, these stages provide ultra-smooth, fast, and high-precision movement without mechanical components like belts or screws.
Based on the operating control method, single axis linear stages are classified into motorized and manual types.
- Motorized Linear Stages
These stages are controlled by motors—usually stepper or servo motors—which automate motion along a single axis. - Manual Linear Stages
Manual stages are adjusted manually, typically using a micrometer or lead screw. These stages are often used in low-tech or experimental settings where automated control isn't necessary, such as basic lab tests or calibration tasks.
What are the key features and applications of a single axis linear stage?
- Linear Motion Control: Enables precise, repeatable motion along one axis (e.g., X, Y, or Z).
- High Precision: Achieves fine positioning with minimal backlash, making it a perfect fit for applications that demand accuracy.
- Load Capacity: Designed to support different weight loads, depending on the application requirements.
- Applications: Commonly used in optics and photonics.
.