Direct Drive Linear Motor Stages
A direct drive motor stage is a high-precision positioning stage with a motor directly connected to the load. This stage provides highly accurate and repeatable positioning by eliminating mechanical components such as belts or gears, which can introduce backlash and wear over time. Below is a selection of direct drive stage and linear motor stage products from our portfolio, and each can be modified and configured to meet your specific needs. Contact us if you need assistance identifying the right motion solution for your application.
Direct Drive Stage Products
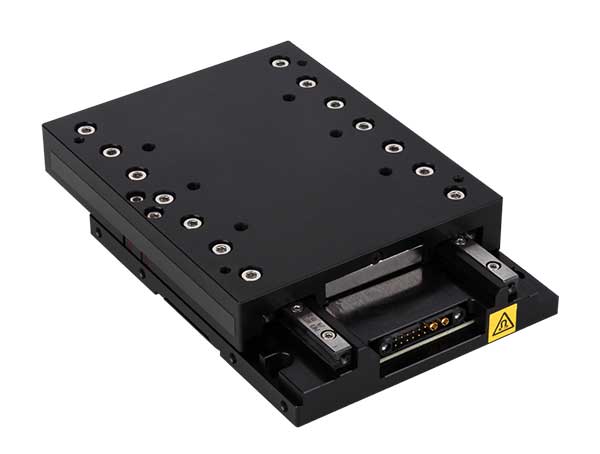
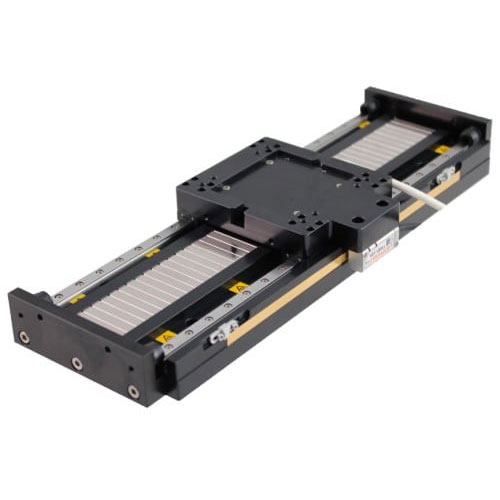
The SmartStage direct drive linear motor stage offers high performance and includes an innovative built-in controller right inside the stage.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 200 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The SmartStage XY Monolithic stage, is a linear motor stage in a low-profile XY form factor, with physically integrated controller, designed for precision positioning.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 75 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 12 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload (kg) | 10 kg |
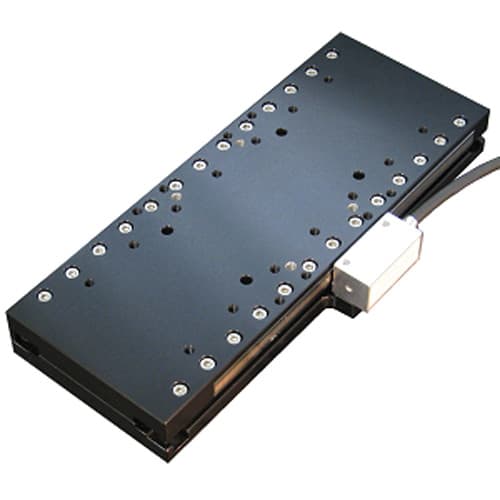
The SmartStage single axis direct drive linear motor stage is our single axis linear stage with a built-in controller, available in multiple travel sizes and options.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 200 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The SmartStage™ Open Frame XY is the first open aperture linear motor stage with an embedded controller physically integrated inside the stage.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 115 x 75 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | ≤ 10 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 0.8 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
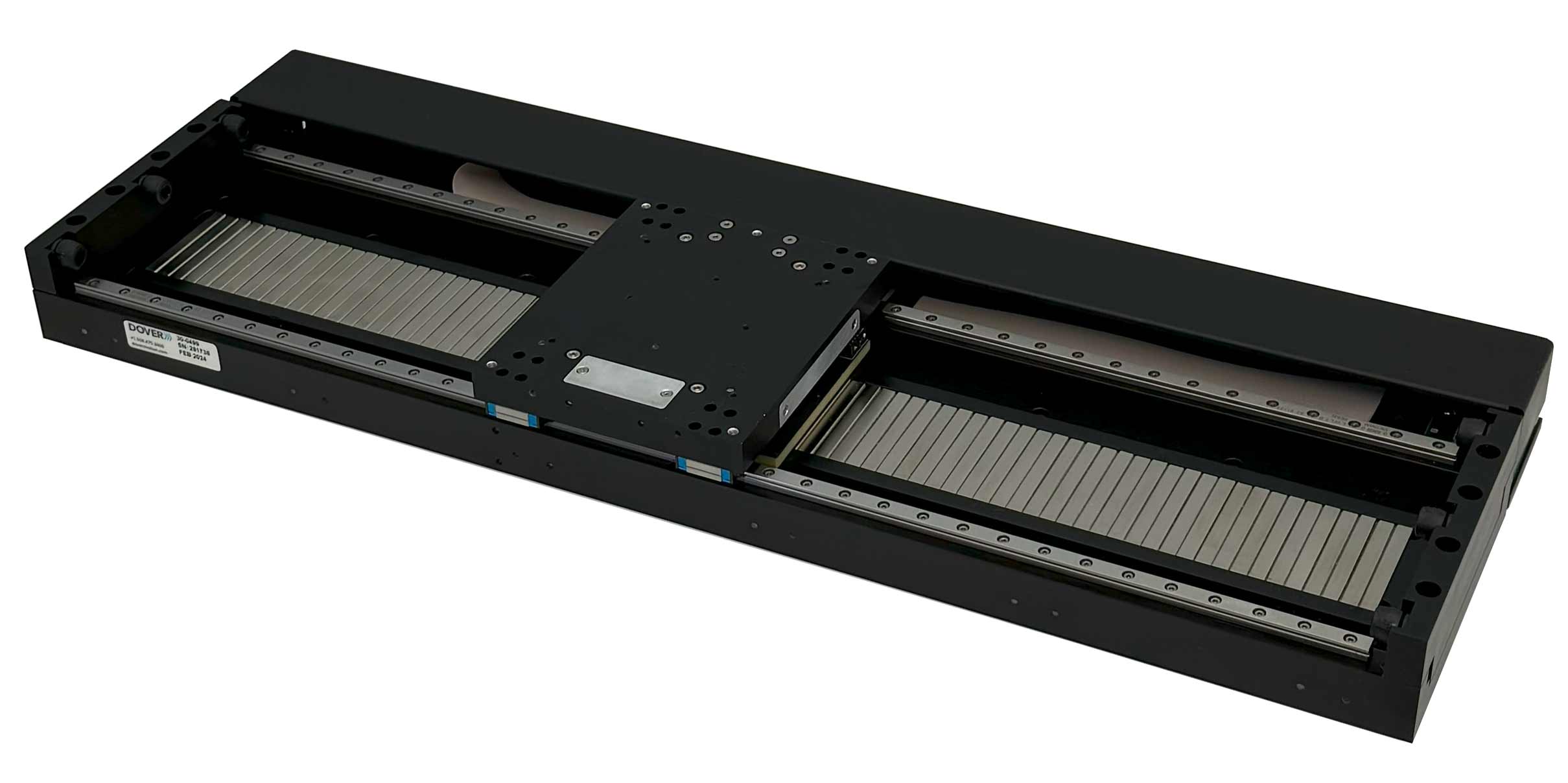
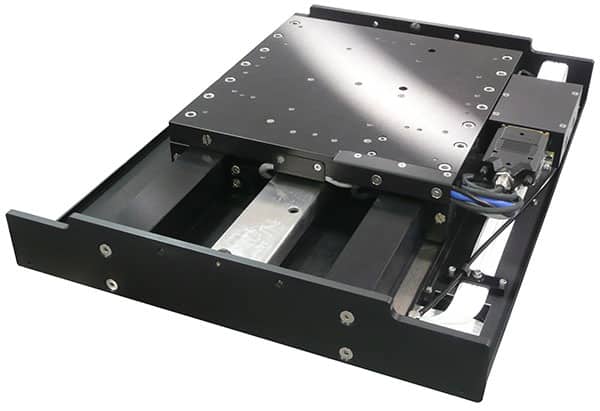
The SmartStage Shuttle is a long travel linear stage, which provides linear motor precision and throughput for XY stage applications.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 200 - 500 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 5 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 1.2 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
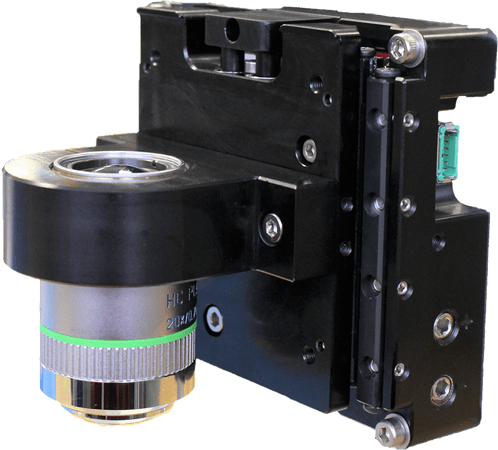
The DOF series objective focusing stage has been optimized for optical microscopy applications. It eliminates alignment headaches.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 5-9 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 1.25 nm |
| 2 | Repeatability | < 50 nm |
| 3 | Bandwidth | > 225 Hz |
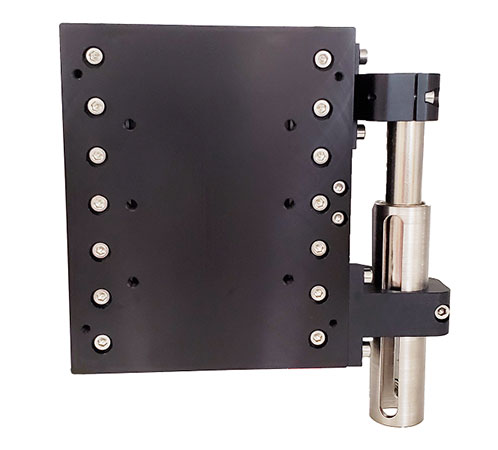
The SmartStage Z-50 provides a unique combination of travel distance, and precision, for vertical Z stage applications.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resolution | 5 nm |
| 2 | Accuracy | 10 μm |
| 3 | Repeatability | .8 μm |
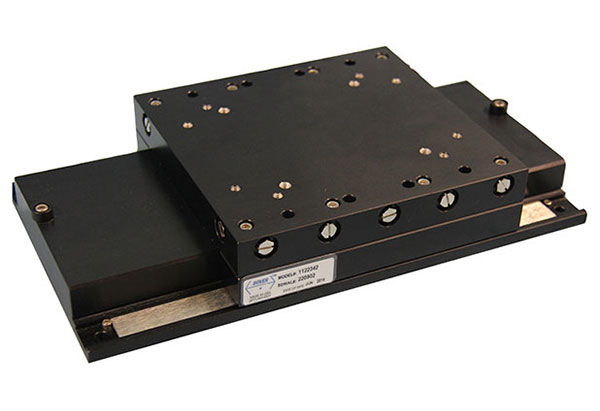
The MMX™ series miniature direct drive stage has a low profile design with high power linear servo motor options.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 25 - 150 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | < ± 3 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.4 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 10 kg |
The MMS™ – Miniature Long Travel Direct Drive Linear Motor Stage ideal for imaging applications where a long travel load/unload axis is required.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 200 - 400 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | < 15 μm |
| 2 | Repeatability | 2 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 12 kg |
The MAG™ series servo linear actuator utilizes a moving magnet design and linear servo motor.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 50 - 250 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 3 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.5 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 75 kg |
The Airglide™ air bearing direct drive stage design uses precision stiff air bearings for large payloads.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 150 - 400 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 4 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.4 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 40 kg |
FiberBeam™ linear air bearing positioners are designed for high accuracy in a low profile.
| wdt_ID | Travel | 20 - 100 mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Accuracy | 2 μm TIR |
| 2 | Repeatability | < ± 0.1 μm |
| 3 | Payload | 15 kg |